Table of Contents
Forced labor remains a pressing global concern, prompting nations to take decisive action to eliminate this egregious violation of human rights from their supply chains. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) is a significant legislative step taken by the United States to combat forced labor in the global supply chain, especially goods originating from the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the UFLPA, the Forced Labor Enforcement Task Force (FLETF), chaired by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS), has been entrusted with the responsibility of developing a comprehensive strategy to prevent the importation of goods produced with forced labor.
The UFLPA Strategy, released on June 17, 2022, guides the enforcement of Section 307 of the Tariff Act of 1930, which prohibits the entry of goods manufactured wholly or partially through forced labor in the PRC. The strategy specifically targets goods originating from the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (Xinjiang) of the PRC and products produced by entities listed on the UFLPA Entity List.
To ensure the effectiveness and relevance of the UFLPA Strategy, the FLETF provides annual updates, and the 2023 updates include changes to various chapters. Notably, Chapter II, which evaluates and describes forced labor schemes and the UFLPA Entity List, has been expanded. Additionally, Chapter V now includes additional resources to prevent goods made with forced labor from entering U.S. ports, and Chapter VII focuses on coordination and collaboration with NGOs and private-sector entities.
Updates to the UFLPA Entity List and Related Plans
The UFLPA's latest update focuses on Chapter II of the UFLPA Strategy, which addresses the evaluation and description of forced labor schemes and the UFLPA Entity List. The UFLPA Entity List plays a pivotal role in identifying entities and facilities involved in forced labor practices. The list includes various categories of entities, such as those in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (Xinjiang) that mine, produce, or manufacture goods with forced labor, entities working with the Xinjiang government to recruit forced labor, entities exporting goods produced by listed entities to the United States, and facilities that source material from Xinjiang for government-labor schemes using forced labor.
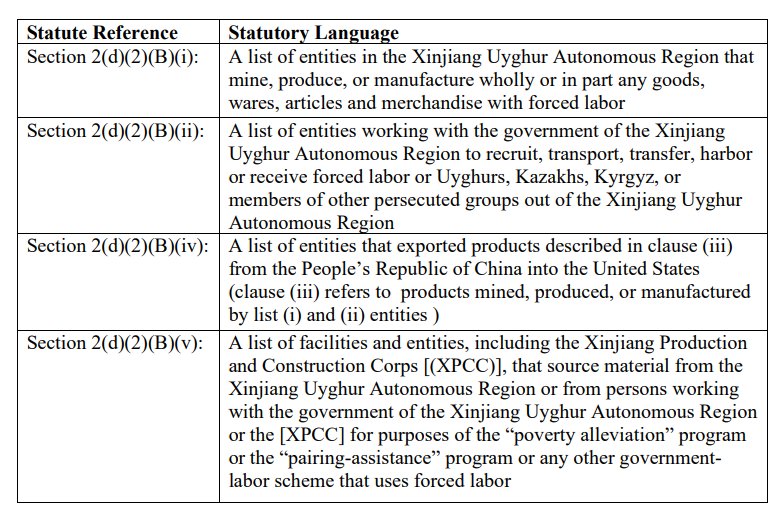
The FLETF, through comprehensive research and collaboration with multiple agencies, has identified and consolidated entities into the UFLPA Entity List. This list serves as a critical enforcement tool, subjecting listed entities to the UFLPA's rebuttable presumption, which prohibits their products from entering the United States under 19 U.S.C. § 1307. The FLETF's work included referencing information from CBP's Withhold Release Orders for goods produced with forced labor in Xinjiang and the Entity List maintained by the Department of Commerce's Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS).
Strengthening High-Priority Sectors: Certain sectors are more susceptible to forced labor practices due to their nature or location. The U.S. strategy involves the identification and prioritization of these sectors for targeted enforcement efforts. By concentrating resources on sectors with higher risk, the U.S. can maximize its impact in eradicating forced labor from critical industries.
Collaboration with NGOs and the Private Sector: Engagement with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and the private sector is indispensable for effective implementation. These stakeholders provide valuable insights, expertise, and on-ground information that contribute to identifying instances of forced labor. Collaboration fosters a collective approach, ensuring that efforts to eliminate forced labor are comprehensive, well-informed, and adaptive.
Enhanced Resources and Capacity Building: To combat the multifaceted challenges posed by forced labor, resource allocation and capacity building are imperative. The U.S. strategy involves the continuous enhancement of resources, both human and technological, to effectively detect and prevent the importation of goods produced with forced labor. This includes investments in advanced screening methods and technologies.
The implementation of the UFLPA Strategy requires significant resources and coordination among multiple agencies. The FLETF, established by the USMCA Implementation Act and Executive Order 13923 in 2020, plays a central role in monitoring and reporting on the U.S. enforcement of 19 U.S.C. § 1307. The FLETF's responsibilities include developing and updating the UFLPA Strategy, maintaining the UFLPA Entity List, and engaging with NGOs and the private sector to ensure effective implementation.
International Cooperation and Advocacy: Forced labor is a global issue, transcending borders and affecting multiple nations. The U.S. recognizes the interconnectedness of supply chains and aims to collaborate with other nations to collectively address this challenge. Through diplomatic channels, international organizations, and bilateral agreements, the U.S. will advocate for the adoption of stringent measures against forced labor.
Heightened Public Awareness and Engagement: Raising public awareness about the consequences of forced labor is instrumental in garnering support for the cause. The strategy includes public campaigns, educational initiatives, and platforms for concerned individuals, civil society groups, and members of Congress to actively participate in the fight against forced labor.
Robust Enforcement of UFLPA Provisions
The UFLPA reinforces the prohibition against the importation of goods produced with forced labor. Rigorous enforcement of these provisions is a cornerstone of the strategy. Importers found to be in violation of UFLPA regulations will face legal consequences, sending a strong message that the U.S. is committed to holding accountable those who perpetuate forced labor practices. Several key agencies are responsible for various aspects of UFLPA implementation. The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) contributes significantly to the FLETF's interagency efforts by providing expertise on forced labor, supply chain tracing, and due diligence. ILAB co-chairs the UFLPA Entity List Subcommittee, supporting the implementation of the UFLPA. However, ILAB anticipates near- and long-term resource needs to meet ongoing demands. U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) plays a crucial role in enforcing the prohibition of goods made with forced labor. To effectively execute UFLPA requirements, CBP has added positions, invested in enterprise systems and technology enhancements, and improved forced labor case management systems. Additional funding is requested to continue building the Trade and Cargo Academy within the Federal Law Enforcement Training Center (FLETC) facility and to sustain internal capabilities enhancements. U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) Homeland Security Investigations (HSI) conducts criminal investigations related to forced labor ventures with a nexus to the United States. HSI, supported by the Counter-Proliferation and Criminal Division (CCHT), requires increased staffing to respond to and investigate forced labor and counterfeiting crimes at ports of entry.
Conclusion: The latest update to the UFLPA Strategy represents the United States' unwavering commitment to eradicating forced labor from global supply chains. By identifying and addressing forced labor schemes through the UFLPA Entity List and related plans, the U.S. seeks to ensure that products made with forced labor do not enter the country. However, addressing this complex issue requires sustained resources and collaboration among various agencies and stakeholders. The U.S. remains resolute in upholding human rights and promoting ethical trade practices to build a fair and just global economy.