Table of Contents
What Is CNS 15663?
CNS 15663, also known as Taiwan RoHS, is a voluntary conformity standard implemented by the Bureau of Standards, Metrology and Inspection (BSMI) under Taiwan’s Ministry of Economic Affairs. Released in 2013, this regulation aims to control and reduce six hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) sold or imported into Taiwan.
Restricted Substances Under Taiwan RoHS
Taiwan aligns closely with EU RoHS 2, restricting these six substances:
📌 Thresholds apply per homogeneous material.
Taiwan RoHS Scope: Products Covered Under CNS 15663
Products with operating voltages below 1000V AC / 1500V DC are covered, including:
- Information Technology Equipment (e.g., computers, laptops, printers, monitors)
- Telecommunications Equipment (e.g., phones, mobile devices, routers)
- Consumer Electronics (e.g., TVs, cameras, audio/video equipment)
- Lighting Equipment (e.g., lamps, luminaires)
- Electrical & Electronic Tools (e.g., drills, saws, soldering equipment)
- Toys, Leisure, & Sports Equipment (e.g., electronic toys, gaming consoles)
- Medical Devices (e.g., monitoring equipment, diagnostic devices)
- Monitoring and Control Instruments (e.g., meters, gauges)
- Automatic Dispensers (e.g., vending machines, ATMs)
- Industrial Equipment (e.g., manufacturing machinery, laboratory equipment)
- Other equipment covered by CNS 3765, CNS 14408, and CNS 14336-1
Taiwan RoHS Exclusions:
- EEEs not reliant on electricity as the primary power source
- EEEs not requiring electrical components for their primary function
- EEEs that are part of other products
- Batteries
- Large-scale stationary industrial tools
- Annex C of CNS 15663 provides additional details on exemptions.
- Annex D of CNS 15663 lists 37 conditions for exemption from concentration limits.
Taiwan RoHS Compliance Assessment: Self vs Third-Party
Option 1: Self-Declaration
- Conduct in-house or supplier-based testing
- Compile material declarations and reports
- Maintain full documentation on request
Option 2: Third-Party Testing
- Engage accredited labs or certification bodies
- Receive formal compliance certificates
- Ensures credibility during BSMI audits
💡 Pro Tip: Use compliance automation tools to manage supplier data, validate results, and generate technical files on demand.
What Is BSMI Certification Approval?

BSMI (Bureau of Standards, Metrology and Inspection) manages formal certification for regulated products.
Inspection Mark Requirements:
- Display RoHS logo next to your inspection number
- Mark “RoHS” or “RoHS (Pb, Cd)” depending on concentration status
Labeling Format:
- "R", "D", "T", "Q", or "M" + 5-digit unique ID
- Example:
R12345 - RoHS
Interpretation:
RoHS= Fully compliantRoHS (Cd, PBDE)= Exceeds limits for Cd and PBDE (declared use)

BSMI Approval Procedures (3 Routes)
1. Registration of Product Certification (RPC)
- Submit documentation for full product certification
- Enables product tracking and verification
2. Batch-by-Batch Inspection
- Used for limited import volumes
- Batches tested and inspected before approval
3. Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
- Manufacturer self-declares compliance
- Must align with technical documentation
- Used in combination with inspection mark

⚠️ Internal testing alone isn’t accepted for all categories — assess your product type before choosing a pathway.
Taiwan RoHS Hazardous Substances Marking: What You Must Disclose
If your product exceeds substance thresholds:
- Provide a hazardous substances table by component
- Place marking on product body, packaging, or user manual
- If details are online, include website URL on the label
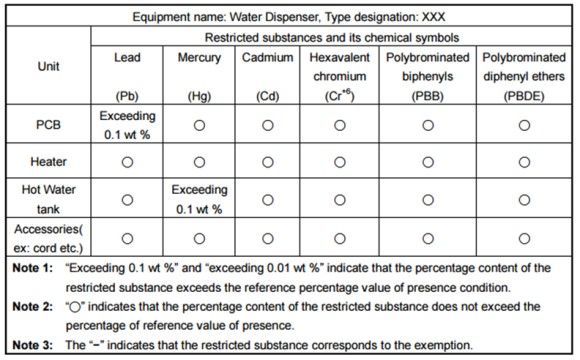
Taiwan RoHS Table Sample:
| Component | Pb | Cd | Cr⁶⁺ | PBB | PBDE | | ----------- | -- | -- | ---- | --- | ---- | | Motherboard | ○ | - | ○ | - | ○ |
Symbols:
○= Compliant-= Exceeds limit, disclosed
Why Taiwan RoHS Matters in 2025
- Growing market: Taiwan is a major EEE importer
- Regulatory alignment: Based on EU RoHS but enforced locally
- Brand credibility: Compliant labeling builds trust with buyers and regulators
- Risk reduction: Avoid fines, product holds, or import rejections
Acquis Makes Taiwan RoHS Seamless
Staying on top of Taiwan RoHS documentation can be time-consuming. Acquis simplifies it by:
- Automating supplier engagement
- Validating restricted substances
- Generating technical documentation (CNS 15663 aligned)
- Supporting DoC, RPC, and hazardous labeling workflows
Schedule a strategy call today to streamline your Taiwan RoHS compliance.
Get compliant. Stay ahead.
