Table of Contents
Full Material Disclosure (FMD): What It Means for Compliance Teams
Material compliance is no longer an option—it’s a requirement.
With increasing global regulations like REACH, RoHS, TSCA, and conflict minerals, companies need accurate Full Material Disclosure (FMD) to ensure compliance and avoid supply chain risks.
FMD ensures that all materials—including hazardous substances—are disclosed, allowing manufacturers to manage regulatory requirements proactively. Failure to comply? Expect regulatory penalties, supply chain disruptions, and lost business opportunities.
Why FMD Matters
- Regulatory Pressure: Non-compliance can lead to fines and supply chain restrictions.
- Market Demand: OEMs and suppliers require transparent material data.
- Risk Management: Without proper FMD, companies risk sourcing restricted materials.
FMD Standards: IPC-1752A, IPC-1754 & IEC 62474
To standardize compliance reporting, three major frameworks are in use today:
Each framework provides a structured way to report material content—but choosing the right one depends on your industry and compliance obligations.
IPC-1752A: Standardizing Electronics Material Declarations
Key Features:
- Used for RoHS & REACH , TSCA (Toxic Substances Control Act), Conflict Minerals, PFAS, EU POPs, compliance data exchange.
- Supports supplier-to-manufacturer reporting on product materials.
- Four levels of disclosure—from simple compliance statements (Class A) to Full Material Disclosure (Class D).
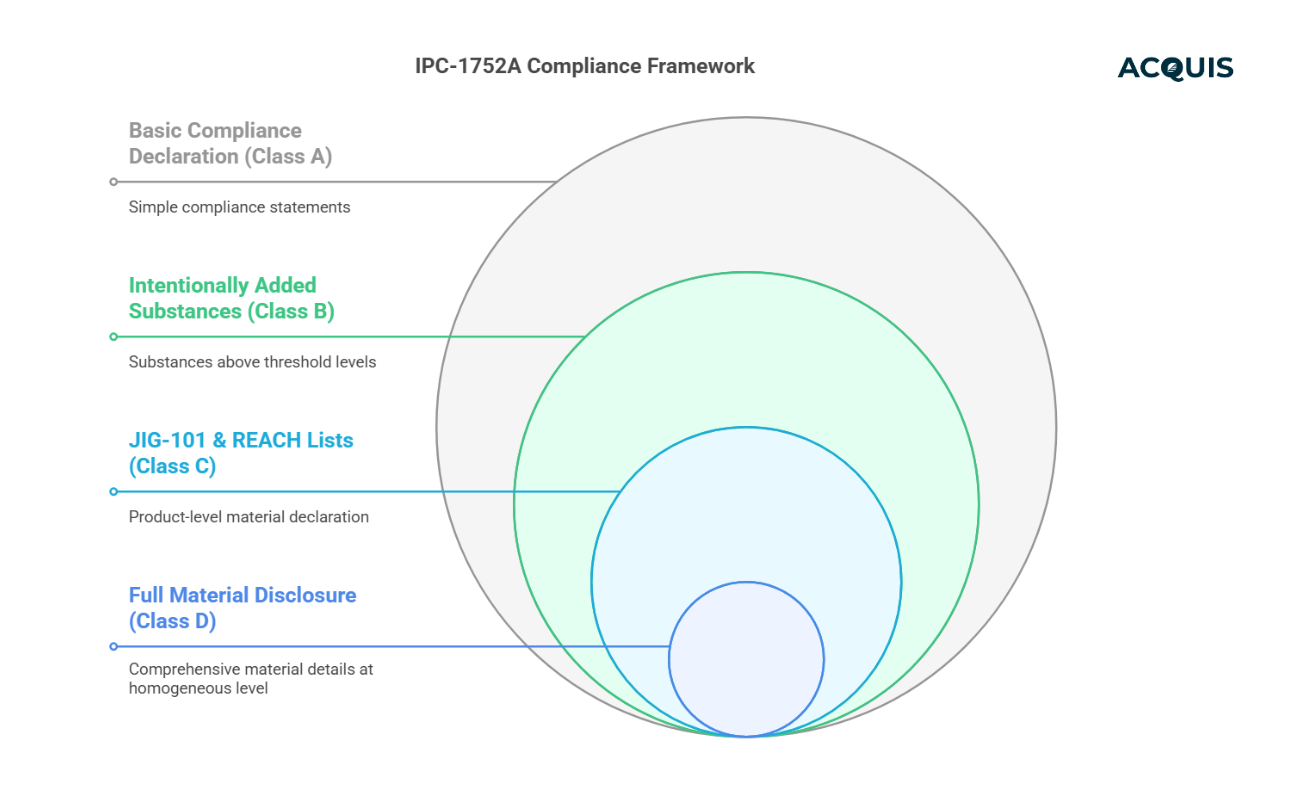
Key Takeaway:
If your company supplies electronic components, IPC-1752A compliance is a must—especially for EU & U.S. regulations.
IPC-1754: The Aerospace & Defense Industry Standard
The Aerospace and Defense sector requires strict compliance with EU RoHS, REACH, TSCA, and other hazardous material regulations. IPC-1754 provides a standardized format for suppliers to report material data, ensuring transparency throughout complex, multi-tier supply chains.
How IPC-1754 Works
- Three levels of material disclosure, from basic compliance to Full Substance Declarations.
- Used to report substances in materials & manufacturing processes.
- Reduces risk of non-compliance with EU & U.S. defense regulations.
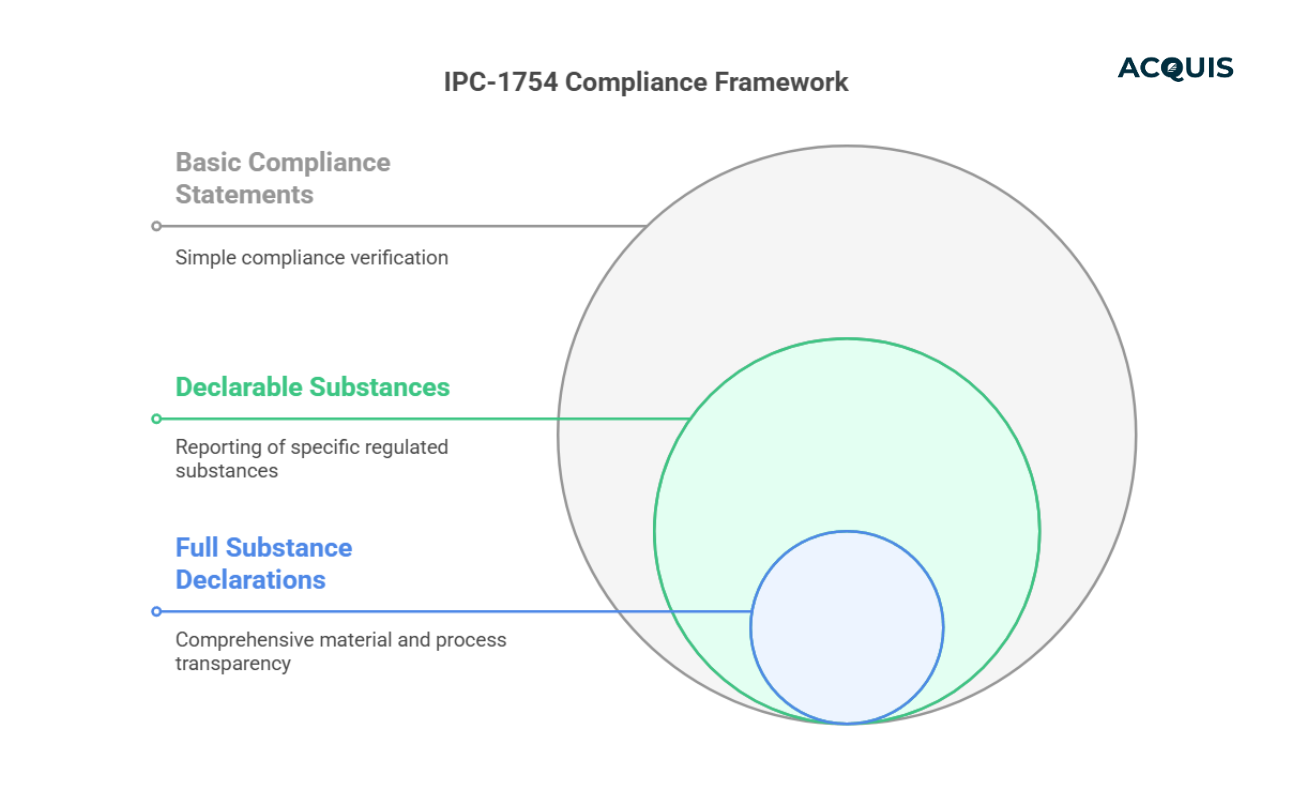
Key Takeaway:
If you manufacture aerospace or defense components, IPC-1754 is essential to ensure regulatory compliance across multi-tier supply chains.
IEC 62474: Global Standard for Hazardous Substance Disclosure
IEC 62474 provides a universal format for reporting hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (EEE).
Why IEC 62474 Matters
- Ensures compliance with RoHS, REACH, and Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) regulations.
- Requires structured XML-based reporting for material declarations.
- Covers substances listed in the Declarable Substance List (DSL).

Key Takeaway:
IEC 62474 is a critical compliance tool for electronics manufacturers, helping streamline global regulatory reporting.
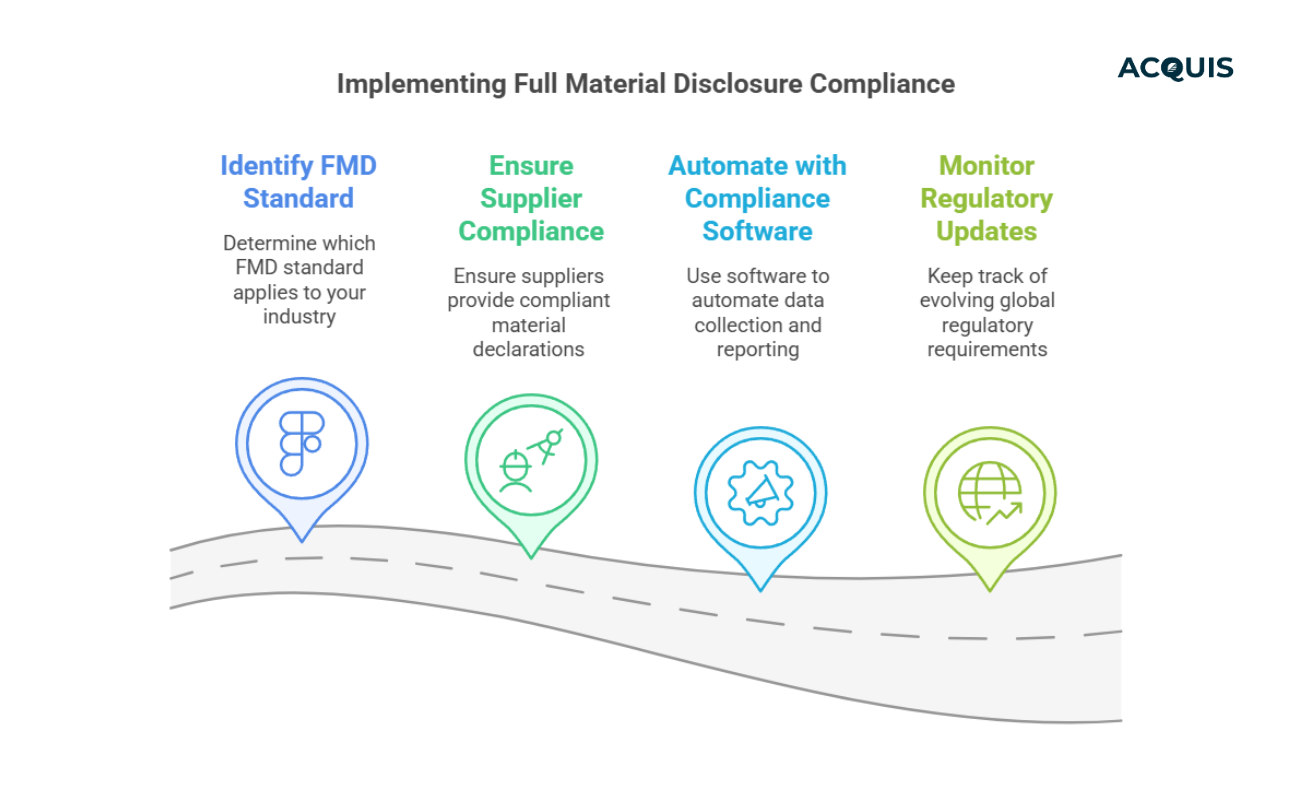
What Companies Need to Do NOW
Regulatory enforcement is tightening. If your company hasn’t established a Full Material Disclosure (FMD) process, it’s time to act.
- Identify which FMD standard applies to your industry (IPC-1752A, IPC-1754, IEC 62474).
- Ensure suppliers provide material declarations that meet compliance requirements.
- Use compliance software to automate data collection and reporting.
- Monitor global regulatory updates—requirements are constantly evolving.
Final Thoughts
FMD is no longer just a best practice—it’s a business necessity. Companies that fail to comply with REACH, RoHS, and global hazardous material regulations face serious risks, including:
- Regulatory fines
- Supply chain disruptions
- Lost contracts with OEMs & defense agencies
Manufacturers that proactively manage Full Material Disclosure will gain a competitive advantage.
Need Help with Compliance?
Acquis Compliance provides FMD solutions to streamline regulatory reporting. Contact us today to ensure your supply chain remains compliant.



