Table of Contents
As we become more aware of the impact of greenhouse gas emissions on the planet, companies are taking a closer look at their carbon footprint. The GHG Protocol Corporate Standard classifies a company’s GHG emissions into three ‘scopes’ - Scope 1, Scope 2 & Scope 3 emissions.
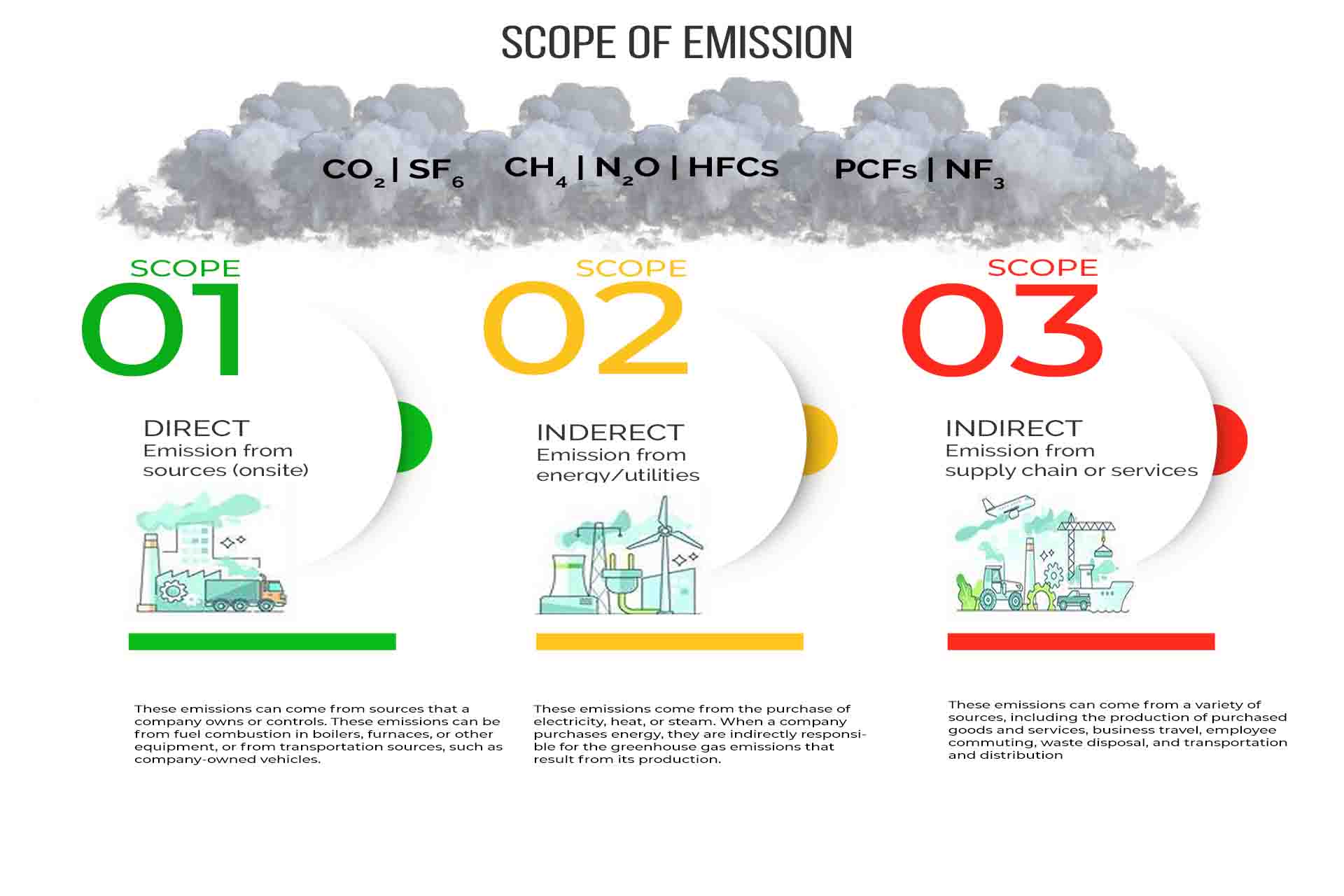
What are Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3 Carbon Emissions?
-
Scope 1 carbon emissions are direct emissions that come from sources that a company owns or controls. These emissions can be from fuel combustion in boilers, furnaces, or other equipment, or from transportation sources, such as company-owned vehicles.
-
Scope 2 carbon emissions are indirect emissions that come from the purchase of electricity, heat, or steam. When a company purchases energy, they are indirectly responsible for the greenhouse gas emissions that result from its production.
-
Scope 3 carbon emissions are all other indirect emissions that occur in the upstream and downstream activities of an organization. These emissions can come from a variety of sources, including the production of purchased goods and services, business travel, employee commuting, waste disposal, and transportation and distribution.
Why Measure Scope 3 Carbon Emissions?
Scope 3 emissions are more complex and can be more challenging to measure, as they are indirect emissions that occur outside a company's immediate control. These emissions can result from the entire life cycle of a product, from its production and distribution to its use and disposal. This includes emissions generated by suppliers, transportation, and waste disposal. In other words, if a company purchases materials from a supplier who generates carbon emissions during production or transportation, these emissions are categorized as Scope 3 emissions.
Measuring scope 3 carbon emissions is important because it helps businesses and organizations understand where their emission hotspots are across their value chain. By identifying these hotspots, companies can prioritize reduction strategies, identify sustainable suppliers, and inform decision-making across procurement, product development, and logistics teams. Measuring scope 3 emissions can also encourage product innovation and engagement with employees to reduce emissions from business travel and employee commuting.
The impact of Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions on businesses and the environment is significant. According to the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, Scope 1 and 2 emissions are often the most significant sources of carbon emissions for businesses. However, Scope 3 emissions can be up to 15 times larger than a company's Scope 1 and 2 emissions combined.
Benefits of Addressing Carbon Emissions:
Addressing scope 1, 2, and 3 carbon emissions can have significant benefits for businesses and organizations. By doing so, they can:
- Meet changing regulatory requirements
- Prioritize reduction strategies to reduce their carbon footprint
- Identify sustainable suppliers and encourage suppliers to reduce their own carbon footprint
- Inform decision-making across procurement, product development, and logistics teams to deliver the most significant emission reductions
- Encourage product innovation to create more sustainable and energy-efficient products
- Advance their climate strategy to create genuine, quantifiable, and visible change
- Positively engage with employees to reduce emissions from business travel and employee commuting
- Communicate a comprehensive footprint and progress with stakeholders, such as constituents and communities
- Contribute to national efforts towards achieving Net Zero.
Measuring and reducing carbon emissions can have significant benefits for businesses, including cost savings, improved efficiency, and a positive impact on brand reputation. Understanding Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions is the first step in identifying areas where emissions can be reduced, and in turn, working towards a more sustainable future.
Greenhouse gas(GHG) emissions are a significant contributor to climate change, and businesses and organizations must play a role in addressing this issue. By measuring and addressing scope 1, scope 2, and scope 3 carbon emissions, companies can take concrete steps towards reducing their carbon footprint and contributing to a more sustainable future. The challenge may be significant, but it is essential for businesses to rise to the occasion and take action towards a more sustainable future.
